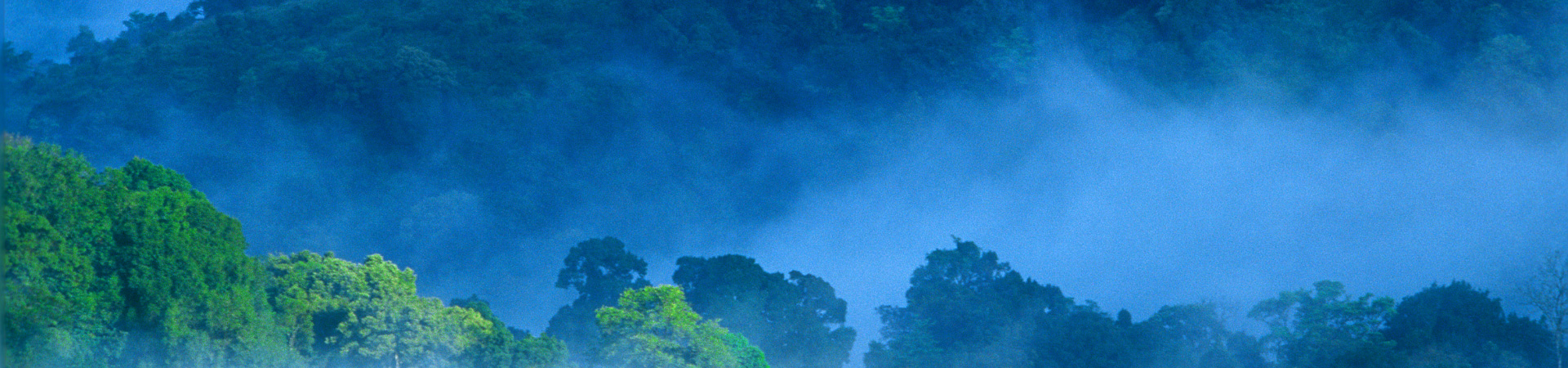
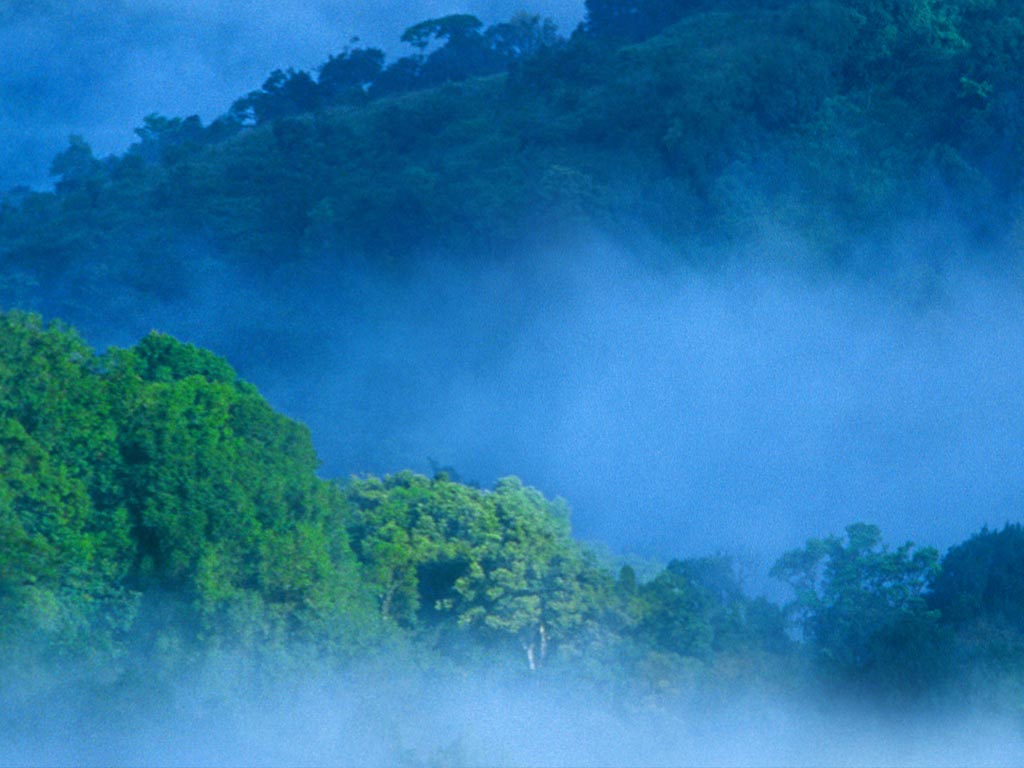


The Periyar Valley was under the reign of the Pandyas who ruled from Madurai until the 12th century. In 1895, the Mullaperiyar dam was constructed. The dam, built across the west-flowing River Periyar, stops the river to form a reservoir. It also resulted in the creation of an artificial lake, which enhanced the charm of the valley. The lake, in the centre of the sanctuary, is the nucleus of the reserve and the place where the elephants and the avifauna come to frolic, to drink water and to cool themselves with dips in the hot months. down to play. By creating this artificial lake, the dam changed the landscape and the features of the valley drastically.
During the 18th and 19th centuries, the reserve was the hunting ground of the Travancore kings. The Kingdom of Travancore comprised most of modern-day southern Kerala, the district of Kanyakumari , and the southernmost parts of the neighboring state of Tamil Nadu. After India's independence, Travancore merged with Cochin to form Travancore-Cochin which again, some time later, joined with Malabar district of Madras State to form Kerala.
Inside the reserve was a palace - the Edapalayam Lake Palace - meant for the guests of the royal family. In 1899, the area was declared as a forest reserve called the Periyar Lake Reserve. This step was taken with the main intention of protecting the hunting area of the kings from the encroachment of tea plantations.
In 1934, the lake reserve was converted into a game sanctuary, the Nellikkampatty Game Sanctuary, on the recommendation of S. C. H. Robinson, the first game warden. The game sanctuary covered an area of about 500 sq km. In 1950, some more area was added to create the Periyar Wildlife Sanctuary. In 1978, the sanctuary was included in the Central Government initiative known as Project Tiger and was renamed the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
Project Tiger, initiated in 1972 to protect the magnificent Bengal Tigers, aims at tiger conservation in specially chosen tiger reserves throughout the country. The Bengal tiger also known as Royal Bengal tiger - the national animal of India - is native to India, Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan.
In 1992, it became part of Project Elephant. Project Elephant was launched by the Central Ministry of Environment and Forests to protect the free ranging populations of wild Asian elephants in various Indian states.
Five years later, in 1996, the India Eco-Development Project too was launched in the reserve. In 2001, the sanctuary was reorganized into two divisions – Periyar East and Periyar West .
Today, the reserve houses at least 40 tigers and hundreds of elephants and its rich jungles with their fascinating biodiversity attract visitors throughout the year.
Biodiversity of Periyar Tiger Reserve  |